Type 2 Diabetes: Everything you need to know
Here is everything you need to know about type 2 diabetes and how to manage it easily
March 19, 2024
Diabetes:
Diabetes mellitus or commonly known as diabetes, is a disorder of the human body where it either fails to produce the insulin required or loses the ability to utilize it to regulate blood sugar levels.
Classes of diabetes:
Diabetes has two classes on the basis of insulin production and uptake.
Type 1 or insulin dependent diabetes is when the body is not capable of producing insulin due to an autoimmune response of the system.
Type 2 or non-insulin dependent diabetes is when the body produces sufficient insulin, however, loses the ability to use it efficiently.
It is a very common to develop type 2 diabetes over the course of a person’s life due to unhealthy eating habits and lifestyles.
What happens in Type 2 diabetes?
In type 2 diabetes, your blood sugar levels become too high resulting in a condition called hyperglycemia.
Your body fails to take up the glucose for utilization due to failure in recognizing the presence of the hormone, insulin.
Why does Type 2 diabetes occur?
Type 2 diabetes can develop due to a few reasons which includes genetics and unhealthy routines.
Genetics can easily play a part in triggering type 2 diabetes either at an early age or even past the age of 45.
Another reason of the disorder can be obesity and consumption of a rather unhealthy diet flooded with unnecessary carbs and sugar.
Physical inactivity can also be a contributing factor in triggering diabetes amid an already unhealthy lifestyle.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes:
Here are some symptoms of type 2 diabetes to look out for:
- Increased and unusual thirst
- Abnormally increased hunger
- Weakness and blurred vision
- Numbness in the hands and feet
- Constant urination
- Wounds take unusually long to heal
- Significant and unexplained weight loss
How to diagnose type 2 diabetes?
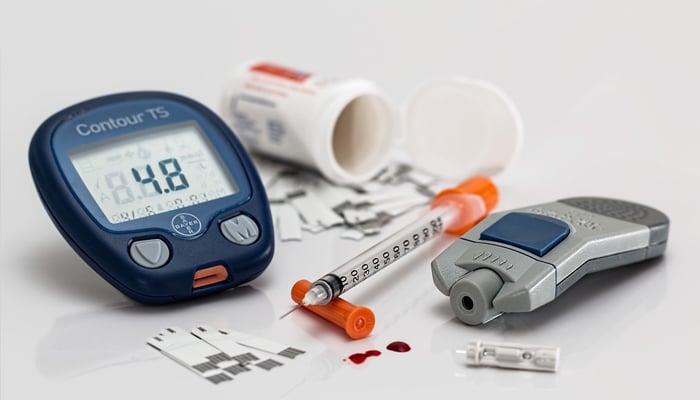
If you experience any of the symptoms above or suspect that you might have diabetes, you can have a glycated haemoglobin test, also known as an A1C test, conducted, which gives you an average reading of your blood sugar levels for the past two or three months.
The normal range of blood sugar is 70 mg/dL to 100 mg/dL, and if your blood reports exceed the limit, it is best to seek medical advise to manage the excess glucose in your body.
Managing type 2 diabetes:
Keeping your diabetes under control is simple as it only requires altering your existing routine into a healthier one.
You need to make sure to monitor your blood sugar as well cholesterol levels to prevent them from fluctuation at dangerously high or low levels.
Eating healthy and exercising well are also ways to keep your blood sugar levels under control amid diabetic conditions.
Any medications prescribed by your doctor or medical health expert are advised to be taken as instructed. You can even work with them to create a diabetic plan to follow in order to manage the disorder.
Even though a diagnosis of diabetes can be scary, rest assured, with a little self-care and caution, you can live a perfectly normal life like any other healthy individual.