How we are fooled into believing in horoscopes
A psychological effect convinces people that bogus statements by fortune-tellers have actual science and calculation behind them
July 06, 2022
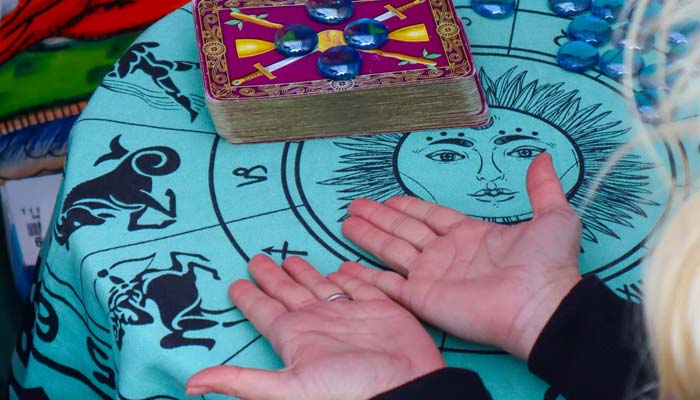

- Fortune-tellers depend on people's cognitive biases.
- Reason people fall into trap is called Barnum effect or Forer effect.
- Why we fall for general descriptions is because we all have the traits, just to varying degree.
Fortune-tellers depend on people's cognitive biases to predict the future, tell them about their personality, and strengthen their belief in horoscopes.
According to a Deutsche Welle report, the reason people fall into the trap of Tarot card readers and vague personality tests is called the Barnum effect or Forer effect.
The Barnum effect is a cognitive distortion that makes people believe that a personality description is accurate when in reality the provided list of traits can apply to anyone.
The effect is named after PT Barnum, a showman who promoted deceptive pranks.
The psychological effect convinces people that the person making the bogus statements has supernatural powers or that there is actual science and calculation behind the predictions.
In the 1950s, Bartram Forer, who was a psychologist, conducted an experiment with his students.
He gave the same text to all students telling them that it was the personalised result of their personality tests. He then asked the students if the personality test had accurately described them. Nearly all the hands went up.
The students then burst into laughter when they read the text aloud.
Forer, therefore, proved the fault in people's judgement and how easy it was to fool them.
Why most of us easily fall for such general descriptions is "because we all have the traits they mention, just to varying degree," the report noted.
"It's not the lack or presence of those characteristics that define us, but to what extent we have them," it said.
"You can sometimes be an introvert and sometimes an extrovert" is like saying "you have a heart and two lungs", the DW report added.
There are many cognitive biases that play a role. For example, a person might neglect negative statements and consider positive statements to be more personal, true, and acceptable.