Understanding Lyme disease: Causes, symptoms, and prevention tips
Symptoms of Lyme disease can vary depending on the stage of the infection
April 24, 2023
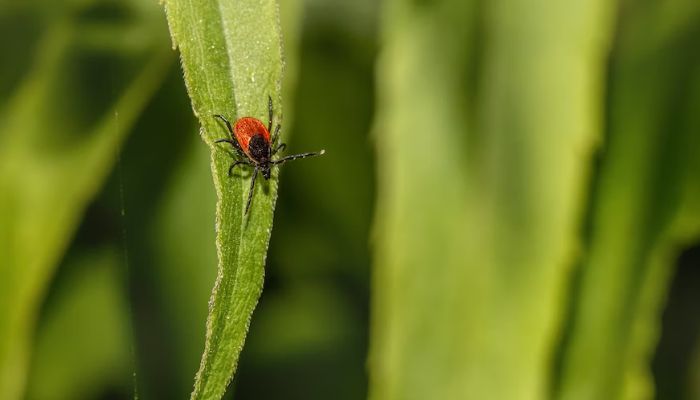

Lyme disease is an infection caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria, which is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks. The ticks that carry the bacteria are mostly deer ticks, also known as black-legged ticks, and they become infected after feeding on animals like deer or mice.
This disease is most commonly found in wooded and grassy areas, especially in the northeastern United States, and has recently been in the news again.
The symptoms of Lyme disease can vary depending on the stage of the infection, but they usually include a circular rash around the bite area, flu-like symptoms, and joint pain.
Diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease
Lyme disease can be challenging to diagnose due to its symptoms resembling those of other illnesses. Blood tests are often used to detect antibodies to the bacteria causing Lyme disease, but they can be inaccurate, especially during the early stages of the disease.
Antibiotics are typically prescribed for the treatment of Lyme disease, and the type and duration of the medication will depend on the stage and severity of the infection. Early treatment can usually be effective in treating Lyme disease and preventing complications.
However, some people with Lyme disease may continue to experience symptoms even after completing treatment. This is known as post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome.
Prevention
To prevent Lyme disease, it's important to take measures to avoid tick bites, such as wearing clothing that covers the body in wooded or grassy areas, using insect repellent, and conducting daily tick checks.
If a tick is found attached to the skin, it's crucial to remove it immediately using tweezers by grasping it as close to the skin as possible and pulling it upward. After removal, wash the affected area with soap and water, and keep an eye out for any signs of a rash or other symptoms.