China unveils next-generation ‘EYESAT' constellation to boost global space traffic management
156-satellite EYESAT initiative signals China’s expanding role in space security
November 28, 2025
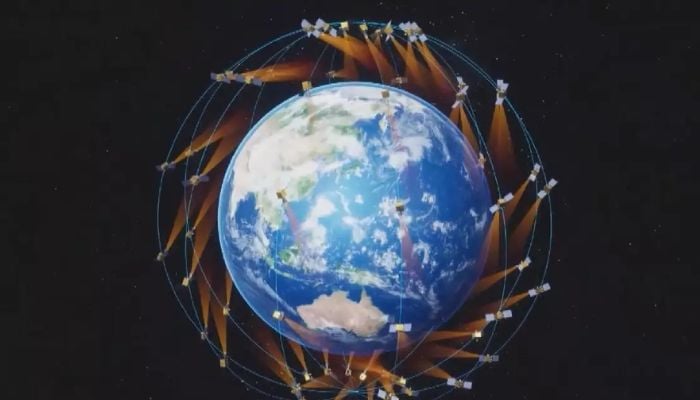

China has announced a new program to build a next-generation space situational awareness constellation designed to improve global space traffic management amid rising concerns over orbital congestion and debris.
The initiative titled as “EYESAT” constellation features an extensive network of 156 satellites scheduled for launch beginning in the first half of 2026.
The EYESAT constellation focuses on establishing a globally covered, rapidly responsive monitoring system in near-Earth orbit.
Once deployed, the network will support real-time detection, monitoring, identification, and cataloging of active satellites, as well as continuous tracking of space debris.
Equipped with advanced sensors involving wide-field, infrared, multispectral, and imaging cameras along with electromagnetic monitoring devices and onboard computing units, the satellite is designed to deliver high-precision data critical for orbital safety.
The program head Hu Yu provides details on the main role of the program is to gather and process data on both operational satellites and debris.
This information will be then shared with active spacecraft to aid them in avoiding potential collisions.
By conducting analysis of orbital paths and predictive modeling, EYESAT is expected to significantly improve early-warning capabilities and reduce the risk of catastrophic in-orbit incidents.
With increasing global space activity and the rising number of satellites, the threats posed by traffic congestion and debris have become urgent issues for spacefaring nations and commercial operators alike.
The data services for space traffic management from EYESAT will help safeguard near-Earth space and enhance long-term sustainability.